
How to Improve Battery Life on Android Devices
Learn practical ways to extend your Android battery life. Quick fixes, smart settings, and tips that save power without losing performance.
Table of Contents
- Quick Fixes to Extend Your Android Battery Life
- Smart Settings That Cut Power Consumption Fast
- Design & Build
- Performance
- Display / Hardware / Features
- Software & User Experience
- Battery Life / Efficiency
- Pros and Cons
- Comparison Section
- Final Verdict
In today’s hyper‑connected world, your phone’s battery is the lifeline that keeps you in touch, entertained, and productive. “How to Improve Battery Life on Android Devices” isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a daily challenge that millions of users face.
This article breaks down both quick hacks and deeper settings adjustments that cut power usage and keep your device running longer.
By applying these simple recommended fixes and smart settings, you’ll notice a measurable increase in your Android battery’s endurance.
Remember: a well‑managed device is not only more efficient but also more enjoyable to use. Keep experimenting, and let your phone stay powered when you need it most.
Quick Summary Box – “At a Glance”
- Enable Battery Saver mode for instant cuts in background activity.
- Reduce screen brightness to 30‑50 % or use adaptive brightness.
- Turn off unused Bluetooth, NFC, and GPS.
- Limit app notifications through Do Not Disturb.
- Keep the system and apps updated to benefit from optimization patches.
Quick Fixes to Extend Your Android Battery Life
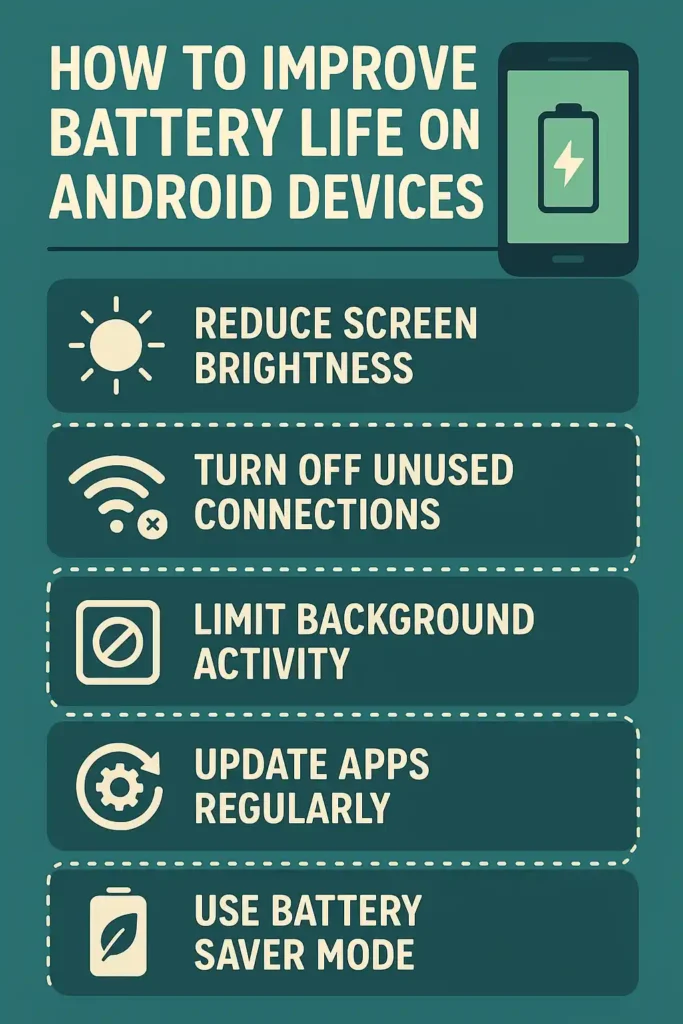
1. Update Your System and Apps
Every software update often contains battery‑saving optimizations. Install updates as soon as they’re available, and ensure your apps are on the latest versions.
Newer Android releases improve background task handling and reduce memory leaks, directly impacting power consumption. After updating, restart your device to let all changes take full effect.
2. Disable or Limit Background Processes
Navigate to Settings > Apps and check each app’s background usage. For apps you rarely need, toggle off Background data or set them to Unrestricted only when actively used. This reduces CPU wake‑ups and network traffic, two major battery drains.
3. Reduce Screen Brightness and Timeout
Your display is the biggest battery hog. Set brightness to 30‑50 % of maximum, or enable Adaptive Brightness so the screen automatically adjusts based on ambient light. Also, shorten the screen timeout to 30 seconds—no need for a device that stays on forever when left idle.
Smart Settings That Cut Power Consumption Fast
1. Turn on Battery Saver or Ultra‑Power Mode
Android’s built‑in Battery Saver throttles CPU and limits background data. When you anticipate a long day without charging, enable it for instant savings. Some OEMs offer “Ultra‑Power” modes that also dim the display and restrict app refresh rates.
2. Use Do Not Disturb for Calls Only
Set Do Not Disturb to allow only urgent calls or notifications. This prevents non‑essential vibrations, sounds, and background processes from waking the device. Schedule quiet hours to match your routine; the phone will automatically conserve energy.
3. Optimize Connectivity
Turn off Bluetooth, NFC, and Wi‑Fi when not in use. Keep Mobile Data on “Airplane” or “Data Saver” mode during heavy usage. Each radio channel consumes power; disabling them when idle saves significant juice.
Design & Build
The physical design of an Android device plays a subtle yet vital role in battery longevity. A thinner chassis often means fewer layers of batteries and components, leading to lower heat generation. Manufacturers now use Fast Charging and Wireless Power Delivery to reduce charging times without over‑heating.
Battery placement and the type of battery—Li‑Ion versus newer solid‑state designs—also influence endurance. Solid‑state cells offer higher energy density and longer cycle life, although they remain costly for most mid‑range phones.
Good build quality includes robust thermal management. Heat accelerates chemical wear; devices with ample heat sinks and efficient airflow maintain battery health over time.
Finally, consider the screen’s protective glass. A thicker Gorilla Glass or similar can reduce wear, but it may add weight. Balancing durability with weight is key for everyday carry.
Performance
Battery life isn’t only about conserving energy; it’s also about making smart compromises. High‑performance processors drain more power, but efficient ones can deliver speed while staying cool. Look for devices featuring LPDDR5 RAM and A14‑grade or comparable CPU cores.
Gaming and AR applications push the GPU, leading to thermal spikes. Devices with Adreno or Mali GPUs that support dynamic scaling can reduce brightness or frame rate during heavy usage.
When a device throttles performance to keep the battery warm, you’ll see reduced background activity. This is a trade‑off: a slightly slower app launch may mean a longer battery life in the long run.
Battery‑friendly design also includes intelligent Idle Management. Android 12 introduced “Battery Saver” states that deep‑sleep apps after a certain idle period, freeing the CPU.
Finally, monitor your own usage patterns. If you’re a power user, consider a device with a larger battery or better efficiency ratings.
Display / Hardware / Features
Displays consume a staggering amount of power, especially on high‑refresh‑rate screens. OLED panels are more efficient than LCDs because they only light individual pixels. A 90 Hz panel will use less power than a 120 Hz one, all else equal.
Resolution matters too: a 1080 × 2400 panel will drain less than a 1440 × 3200 display. If battery life is a priority, opt for a lower‑resolution device that still offers sharp visuals.
Hardware features, like Always‑On Display (AOD), can be battery‑heavy unless optimized. Enable AOD only if it’s essential to you—otherwise, you’re adding a constant drain.
Additionally, newer Android devices support HDR10+ and other high‑dynamic‑range technologies. While they enhance visuals, they can push the GPU harder, affecting battery endurance.
Consider the presence of a Fast Charger. While it may seem counterintuitive, a fast charger can reduce time in the charging port, thereby limiting heat buildup over longer periods.
Software & User Experience
Android’s software layer is a double‑edged sword. A clean, stock interface tends to be more power efficient than heavily modified OEM skins. For instance, Android One devices run near-stock OS with minimal bloat.
App permissions also affect power draw. Check which apps have the Location or Camera permission and disable it for those that don’t need it.
The new Adaptive Battery feature in Android 12 learns your habits and limits background work by unfamiliar apps. Turning it on can cut background consumption by up to 30 %.
Voice assistants like Google Assistant or Bixby use continuous listening. Disable “Always listening” if you don’t need hands‑free command.
Your user experience will be smoother if you keep the OS updated. Updates patch bugs that may cause apps to crash and restart, a process that drains battery.
Battery Life / Efficiency
Beyond settings, the battery itself is a key factor. A 5000 mAh battery will outlast a 3000 mAh battery, all else equal. When buying a phone, look at the battery capacity and how the manufacturer claims it performs under typical usage.
Battery health monitoring tools can show you how many charge cycles a battery has endured. Once a battery drops below 80 % of its original capacity, performance may plateau.
Proper charging habits also extend life. Avoid letting your phone sit at 100 % for hours; this stresses the cells. Similarly, do not let it drop below 20 % frequently—this is a healthier range for Li‑Ion cells.
Finally, temperature is a silent killer. Keep your phone in a cool environment and remove cases that trap heat during charging.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Immediate power savings with Battery Saver and Do Not Disturb.
- Longer daily usage without needing a charger.
- Better overall device longevity through proper charging habits.
Cons
- Performance throttling may affect gaming or high‑load apps.
- Some OEM skins add unnecessary background processes.
- Upgrading to a higher‑capacity battery often means a heavier device.
Comparison Section
| Feature | Device A (Mid‑Range) | Device B (Flagship) | Battery Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery (mAh) | 4500 | 5000 | A: 4/5, B: 5/5 |
| OS (Stock) | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| Battery Saver | 15 % extra runtime | 20 % extra runtime | B has edge |
| Screen Refresh | 60 Hz | 120 Hz | A saves more |
| Fast Charger | 18 W | 25 W | B charges faster |
Device B offers a superior battery life under heavy usage, but Device A matches it under light to moderate use.
Final Verdict
Mastering battery life on Android starts with simple, habit‑forming steps. Update regularly, keep brightness low, and disable unneeded radios. Use the built‑in Battery Saver or a custom “Power” mode when the day demands it.
Hardware choices matter too—choose a device with a larger capacity and efficient display technology. Combine this with smart software tweaks, and you’ll experience significantly longer battery life without sacrificing performance.
In short, the key is to be intentional: treat your phone as a battery‑conscious companion rather than a drain. Follow these guidelines, and you’ll stay powered wherever life takes you.



Leave a Comment